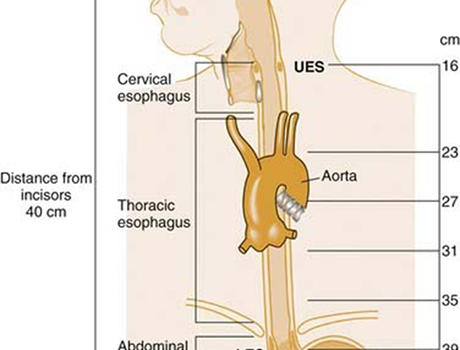
Oesophagus
The esophagus is a tubular, elongated organ of the digestive system which connects
the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is the organ that food travels through to
reach the stomach for further digestion. It follows a path that travels behind the
trachea and heart, in front of the spinal column, and through the diaphragm before
entering the stomach
The bladder, like other parts of the urinary tract, is lined with a layer of cells called the urothelium. This layer of cells is separated from the bladder wall muscles, called the muscularis propria, by a thin, fibrous band called the lamina propria.